Presentation of the Best Practice
Target challenge
- Water for irrigation and food production is not available
- Poor quality of treated water
- High health risk
- Environmental pollution
- Overexploited groundwater
- NCW not valued locally
- Move towards zero discharge at local level
- High treatment cost
- Better selection of Implementation criteria of NCW systems
- Inadequate decisions by decision-makers
- Reclacitrance to use treated NCW
Area Typology
- Urban area
Main beneficiaries
- Water Utilities
- Municipalities
- Farmers
- Management Authorities
Funding
- EU funding
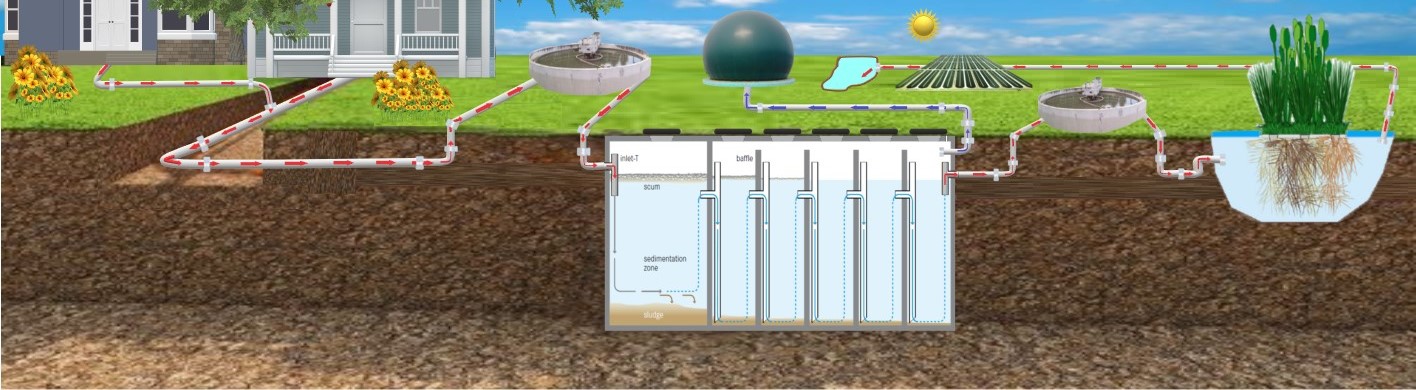
Used technologies / tools
- (i) Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
- (ii) Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR)
- (iii) Anaerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor (ASBR)
- (iv) Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Reactor (AFBR)
- (v) the Anaerobic Filter (AF)
- Anaerobic Fixed Film Reactor (AFFR)
- CWs: Constructed Wetland
- the cost-effective treatment of urban wastewater (with the acronym APOC)
- comprises anaerobic digestion (AD)
- constructed wetlands (CWs)
- a novel solar Raceway Pond Reactor (RPR)
- for final disinfection and removal of organic micropollutants
- (e.g. residual pharmaceuticals and degradation by products, etc.).
Implementation site
NCW type
- Municipal wastewater (MWW)
NCW USE
- Ecosystem
- Toilet Flushing
- Garden Irrigation
- Field irrigation
- Recreation Area
Self-Assessment
TRL : Technology Levels
Obstacles to implementation
- Isuffi cient funding instruments to support solution for NCW
- Lack of public acceptance of water reuse
- Other (Please specify below)
- Lack of funding for the continuous operation of BPs (at demo scale) after the life time of the project The lack of interest by the involved stakeholders/end users (no regulations enforcement concerning the need to treat and reuse municipal wastewater).
Obstacles to funding
How your Best Practice is economically feasible ?
The BP is a self-sustained system since the connection to the grid is not necessary. The necessary energy required is produced by Renewable Energy Sources, including solar (via photovoltaic panels) and biogas, generated by the anaerobic digestion of the organic content of the municipal wastewater. APOC can be implemented using local skills and know-how to provide context-specific sanitation services and get optimum efficiency of the system. Moreover, it can provide a solid byproduct (anaerobic solid digestate) that can be used for land fertilization while APOC treated effluent can be used for urban, industrial, agricultural uses and groundwater recharge.Result of this assessment
A cost benefit analysis will be performed during the next year that will identify the return on investment taking into account the capital, variable (operational), and fixed costs, as well as the environmental benefits.Enviromental impact
SDGs
Validation/upscaling
Potentiel of exploitation/outscaling
Lessons learnt
Highlighted KPI
Technical indicators
Economical indicators
Without consideration of the depreciation period




Social impact of the BP
Jobs created comment: Within AQUACYCLE project, in the context of which the APOC system has been developed and demonstrated, more than 40 jobs have been created by the collaborating partners in five countries (Greece, Malta, Spain, Tunisia, Lebanon).